Transducers, gauges, sensors - Information portal © 2011 - 2025 Use of material is possible by placing an active link
Magneto inductive method of flow measurement
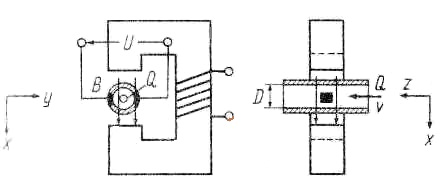
When you move a conductor in a magnetic field under s law of induction in it an electromotive force and an electric current. This effect is used in an inductive flow meter to determine the flow rate. Flowing fluid is identified with the leader, that is, it should have some - a minimum conductivity. According to Faraday's law, the conductive liquid flowing four-cut magnetic field, an electric field. Controlled flow flows through the insulator-coated pipe in the wall which is perpendicular to the magnetic field and the flow of liquid (medium) has two diametrically opposite electrode, which relieves stress. Magnitude of the voltage is proportional to the mean flow velocity of the medium. This voltage is formed by a high resistance source (liquid) with the cable supplied to the transmitter, which amplifies it and carries out further processing. The signal, typically a few millivolts.
The theory of induction flowmeter based on Maxwell's equations.Conductive liquid flows therefore has a certain amount (concentration) of the electric charges. On moving charges Lorentz force and rejects it in the perpendicular direction, which leads to the emergence of electric potential difference (voltage). Magnitude of the voltage is proportional to the flow rate and electrical properties of the liquid (stream).
The output of the desired signal flow is low.In this scheme, there are significant flow measurement noise. They arise due to the asymmetric electrode electrochemical voltage and electrode polarization. This interference can be several times the useful output. To eliminate these shortcomings in the industry in this type of flow meters use a variable or switchable magnetic field. This technique allows you to select the desired signal and to achieve acceptable accuracy.
Diagram of magnetic induction flowmeter:
Home >> Manometers. Pressure gauge >> Magneto inductive method of flow measurement
русский / english
• Information about various converters and sensors of physical quantities, parameters of various physical processes is presented.
• Electrophysical properties and effects in various electrical materials.
• Theory, experimental results, practical application

See also:
CONVERTERS, GAUGES, SENSORS
Information, news, advertising


